Yahtzee History
Yahtzee is a popular dice game of strategy and luck, enjoyed by millions worldwide. First marketed in post-WWII America, its origins trace back to earlier dice games like Yacht. Players roll five dice to achieve specific combinations, aiming for the highest score. Over the decades, Yahtzee has remained a beloved classic, evolving through various editions and digital versions.
When did Yahtzee come out? Modern Yahtzee was commercially released in 1956 by the E.S. Lowe Company. But the game's origins go back much further, with roots in ancient dice games that were played thousands of years ago. Since then, manufacturers have continued to release updated and redesigned versions.
But throughout its history, the spirit of Yahtzee remains constant. It's a game that's easy to learn, yet challenging to master. And that's why it's still one of the most popular dice games in the world. Behold the marvel of Yahtzee history through the ages!
The History of Yahtzee

Yahtzee cup
Yahtzee is far more than a simple game of dice - it is a pillar in the history of gaming, a bridge between ancient games of chance and the structured strategy of the modern era. With its unique fusion of luck, calculation, and tactical foresight, Yahtzee introduced generations to the deeper pleasures of gameplay: weighing risk against reward, mastering probability, and crafting winning strategies under pressure. Since its debut in the 1950s, it has sold over 50 million copies, securing its place as a cornerstone of family gatherings and competitive play alike.
Yet, Yahtzee’s true legacy lies in its remarkable ability to evolve. Across decades, it has transcended the tabletop - reinventing itself through electronic handhelds, captivating mobile apps, and global online platforms. It has not merely survived the march of technology; it has embraced it, adapting to each new medium while preserving the timeless thrill at its core. From living rooms to leaderboards, Yahtzee continues to shape the way we play, teach, and think about games - an enduring testament to its status as one of gaming’s true immortals.
 Origin
Origin
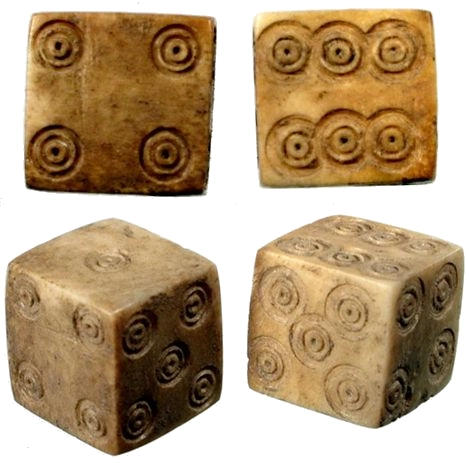

circa 100 CE
Long before Yahtzee emerged, dice were already shaping the way humans played and thought. As some of the earliest tools for generating randomness, dice originated from knucklebones - specifically the astragalus bones of animals - used in prehistoric times. These bones, marked for gaming or divination, eventually evolved into the six-sided cubes we know today. Across ancient civilizations from Egypt to India, dice found their place in recreation, gambling, and early mathematical thinking, laying the groundwork for probability and game theory.
Ancient dice games offered surprisingly rich gameplay experiences. The Egyptian game Senet, dating back to around 3500 BCE, used throwing sticks to guide players across a 30-square board, blending entertainment with spiritual significance. The Romans played Tali, a game involving four dice where combination, like the coveted “Venus” roll, determined scores. Though simpler in form, these games embodied familiar elements of modern dice play: calculated risks, strategic movement, and the thrill of the roll.
These early innovations set the stage for games like Yahtzee. The transformation from knucklebones to structured games reflected humanity’s growing desire to explore chance, pattern recognition, and strategy. Today’s dice games, from board games to digital platforms, carry the legacy of those ancient practices. Every toss of a die is more than a game mechanic - it’s a connection to a tradition that spans millennia, echoing the same excitement and ingenuity that have captivated players since the dawn of civilization.
 in the Modern Age
in the Modern Age

1943
Yahtzee’s modern-day resurrection can be traced back to two key developments in the 1940s - events that, while occurring separately, were ultimately connected through a shared legacy. During World War II, as fuel shortages and financial constraints kept families closer to home, the Leister Game Company in Toledo, Ohio capitalized on the growing demand for home entertainment. As the company observed, “Now that gas rationing has ushered in a back-to-the-home movement, material for home entertainment... is in great demand.”
In response, Leister released a boxed set in 1943 called “Luck - 15 Grand Dice Games,” which included a game called “Yatzie.” Though not yet the game we recognize today, Yatzie was a close predecessor - its rules and structure featured several familiar combinations, though it lacked elements like Three-of-a-Kind and required five sequential dice for both Straights. The game’s name and marketing also reflected a trend of the time: a vague, exoticizing use of a pseudo-Chinese-sounding name, accompanied by stereotypical imagery and themes. This branding leaned into low-level cultural caricatures that were common in mid-20th-century entertainment, reflecting the casual racism and orientalist tropes then prevalent in American popular culture.
And there were some other passages in the rule book that appear odd to the modern dice roller:
- Only 10 scoresheets are included with the game - modern editions typically include ten times as many.
- Players are encouraged to make their own scorecards once they run out; selling extra pads wasn’t a practice yet.
- For two-player games, the rules suggest one player completes their entire game before the other begins.
The success of “Luck” was largely regional, circulated through Toledo’s National Association Service, and while most of its companion games like “Floradora Sextette,” “Black Cat,” and “Help Your Neighbor” faded into obscurity, Yatzie stood out. Its clever balance of luck and scoring strategy left a lasting impression. This earlier version of Yahtzee would later resurface in an unexpected way - through the influence of a wealthy Canadian couple, who encountered a similar dice game during a tour of Tibet in the early 20th century. Fascinated by its blend of chance and strategy, they began playing it regularly during global travels on their private yacht.
Inspired by the game’s ancient roots and elegant simplicity, the couple refined the rules and developed a more structured scorecard, rebranding their version as the “Yacht Game” or “The Yacht at Sea Game.” The name eventually evolved - likely through a combination of oral tradition and the influence of “Yatzie” from the Luck game - into the modern title we know today: Yahtzee. What began as a blend of ancient gameplay and wartime innovation would soon become a global phenomenon, carried forward by both tradition and timely reinvention.
Edwin S. Lowe

1910-1986
When we think of corporate visionaries, certain names spring to mind: Steve Jobs, Thomas Edison, Henry Ford, Walt Disney. But one name that rarely makes the list - though it should - is Edwin S. Lowe, the man who transformed Yahtzee from a private diversion into a household name. In 1956, Lowe was approached by the Canadian couple behind the “Yacht Game,” who were looking for a way to share their elegantly simple dice game beyond the decks of their private yacht. Struck by its balance of chance and strategy, Lowe saw not just a game, but a cultural touchstone waiting to be born. The couple agreed to sell the rights in exchange for the first 1,000 copies of the newly minted game, which they gifted to family and friends who had already fallen in love with it during their travels.
Lowe’s instinct for innovation and branding had deep roots. Born in 1902 in Poland, Lowe immigrated to the United States as a teenager and came of age during the Great Depression, working as a traveling salesman. It was on one of these trips - specifically a visit to a small county fair in Georgia - that he encountered a game called Beano, which involved players covering numbers on a card with dried beans. Captivated by its simplicity and the tension it generated among players, Lowe took a few cards home to Brooklyn, where he introduced the game to friends. During one of these casual sessions, a player accidentally shouted “Bingo!” instead of “Beano” in a slip that would change Lowe’s life. Realizing the potential of the name and the game, Lowe immediately moved to commercialize it. Under his new E.S. Lowe Company, “Bingo” quickly became a national sensation, especially among churches and schools looking for fundraising tools.
By the mid-1930s, Bingo’s popularity had exploded. Lowe’s company was churning out thousands of cards, eventually partnering with a Columbia University mathematician to create over 6,000 unique, non-repeating combinations - a breakthrough that helped legitimize and expand the game even further. This success didn’t just make Lowe wealthy; it gave him a key insight that would shape his approach to future games: a strong foundation in probability and statistical variety could fuel both fun and long-term engagement. It was this belief that made him uniquely receptive to Yahtzee. He recognized in it not only a well-balanced game, but one built on a lattice of mathematical possibilities - each roll of the dice a new iteration of chance, strategy, and human decision-making.

Original 1956 Yahtzee game box.
Yahtzee, however, did not catch on immediately. Though the United States Patent and Trademark Office officially registered the Yahtzee name on March 19, 1957, initial sales were sluggish. Lowe quickly realized that players needed to experience the game firsthand to appreciate its blend of chance and strategy. In response, he pioneered a grassroots marketing strategy: the Yahtzee party. He hosted events across North America, inviting people to play, socialize, and spread the word. The tactic worked - Yahtzee became a word-of-mouth phenomenon, an early example of a viral hit long before the internet made such things common. From these humble beginnings, Lowe’s second major gaming legacy was born.
 in the 1970s
in the 1970s

1973
By the early 1970s, Edwin S. Lowe had accomplished more than most entrepreneurs could dream of. Having created one American classic in Bingo and elevated another in Yahtzee, Lowe was ready for a new chapter. Ever the renaissance man, his interests stretched well beyond the gaming table. In 1973, he sold the E.S. Lowe Company to the Milton Bradley Company for a reported $26 million - roughly $174 million in today’s dollars. The sale allowed him to pivot into new ventures, including producing Broadway plays and even opening a hotel on the Las Vegas Strip. While Lowe moved on, the company he built continued to thrive under new ownership, thanks largely to the momentum Yahtzee had gathered through his innovative, people-first marketing tactics.
Under Milton Bradley’s stewardship, Yahtzee entered what can only be described as its golden era. The company’s deep distribution channels and seasoned marketing apparatus gave the game a level of exposure previously unimaginable. The timing was ideal. Board games were becoming more than just rainy-day pastimes - they were quickly establishing themselves as staples of family life and social gatherings. With a product that balanced luck, skill, and universal appeal, Milton Bradley seized the moment to turn Yahtzee into a permanent fixture on American shelves.
The results were swift and substantial. In just two years after the acquisition, annual sales from the former E.S. Lowe product lines skyrocketed from $6 million to over $23 million. Part of this boom was driven by chess mania following the 1972 Fischer-Spassky championship, but Yahtzee played a major role in sustaining the company’s growth. In fact, Yahtzee became more than a game - it became a cultural ritual. Families played it around kitchen tables, friends packed it for road trips, and teachers began to notice its surprising educational value. The game’s mechanics - built around probability, arithmetic, and decision-making - made it a natural fit in classrooms and community centers alike.
To keep the momentum going, Milton Bradley introduced a steady stream of Yahtzee variations throughout the decade. Travel Yahtzee appeared in 1970, catering to an increasingly mobile public. Triple Yahtzee followed in 1972, offering advanced gameplay with a more intricate scoring system. In 1974, Challenge Yahtzee upped the ante again, and in 1978, Word Yahtzee creatively fused dice with wordplay to appeal to language lovers. These spin-offs helped the brand evolve while remaining true to its core identity.

Wort Yahtzee
1979, Germany
Milton Bradley also wasn’t shy about modern marketing. A major coup came in 1974 when the company featured Tony Randall and Jack Klugman - the stars of the hit show The Odd Couple - on the box of Challenge Yahtzee. The celebrity endorsement gave Yahtzee a pop culture sheen and helped introduce it to new demographics.
Behind the scenes, Milton Bradley’s acquisition strategy was transforming the landscape of American gaming. With James Shea Jr. at the helm as president (and later CEO), the company shifted its focus toward acquiring successful properties rather than developing them in-house. This model - buy proven hits, scale them fast - worked brilliantly. But the acquisition tide would soon rise even higher.
 in the 1980s
in the 1980s

1980
As the 1980s unfolded, Yahtzee found itself once again at the heart of a major corporate transformation. In 1984, Hasbro - a rising force in the toy and game industry - acquired the Milton Bradley Company. At the time, Milton Bradley was the fifth-largest toymaker in the United States, with Hasbro just behind it at number six. The merger created a new industry giant, and within a few short years, this newly combined entity had eclipsed Mattel to become the world’s largest toy company.
Despite the sweeping consolidation, Yahtzee emerged from the transition as strong as ever. Now under Hasbro’s expansive corporate umbrella, the game continued to enjoy mass-market visibility and sustained popularity across generations. It stood firm even as the broader toy landscape began to shift, especially with the rapid rise of video games and electronic entertainment that threatened to sideline traditional board games. If anything, Yahtzee’s resilience proved that simple mechanics, tactile play, and social connection still held powerful appeal.
Hasbro, in keeping with its growth-focused ethos, pushed to maximize Yahtzee’s potential across every conceivable medium and market segment. New variations of the game were developed throughout the decade in an effort to keep the brand fresh and engage new audiences. Among them was Jackpot Yahtzee, released in 1980, which sought to channel the thrill of casino-style gameplay with a dice-based twist. This was followed by Casino Yahtzee in 1986, further leaning into the glitz and glamor of gambling themes.
While these variants drew attention for their novelty, neither achieved lasting success. Their lukewarm reception underscored an essential truth about Yahtzee: its genius lies in its simplicity. The allure of the original game, with its elegant balance of luck and strategy, was difficult to replicate or improve upon. Still, the willingness to experiment demonstrated the flexibility of the Yahtzee framework and Hasbro’s commitment to evolving the brand without sacrificing its identity.
The brand’s experimentation didn’t stop at tabletop spin-offs. In 1988, Yahtzee made a surprising leap to television with the debut of Yahtzee: The Game Show, hosted by Peter Marshall of Hollywood Squares fame. It was an ambitious project aimed at tapping into the era’s booming game show craze. Though the show was fresh and promising, it was short-lived. Internal conflicts, executive clashes, and legal troubles behind the scenes ultimately led to its abrupt cancellation within the same year. Despite the drama, the very existence of a Yahtzee game show hinted at the game’s cultural saturation - it had moved beyond the kitchen table into new, uncharted arenas.

Yahtzee
1982, Netherlands
Even as the televised version fizzled, Hasbro was planting the seeds for Yahtzee’s digital future. The groundwork was laid in the late ’80s, and by the 1990s, the game would go fully virtual. But even before that transition, the idea of Yahtzee as more than a physical board game - something that could be digitized, televised, and reinvented -was already taking shape.
Through the corporate mergers, unsuccessful variants, and bold media experiments, one fact remained clear: Yahtzee wasn’t just surviving the rapidly changing gaming industry - it was adapting, evolving, and laying the foundation for decades to come.
 in the 1990s
in the 1990s

1995
The 1990s marked a transformative period for Yahtzee, characterized by a blend of traditional expansion and adaptation to emerging digital technologies. This decade saw the game navigate the changing landscape of entertainment while maintaining its core appeal.
The decade began with the introduction of Showdown Yahtzee in 1991, continuing the trend of creating variations on the classic game. This new iteration aimed to inject fresh excitement into the Yahtzee brand, appealing to players seeking a novel twist on the familiar format. While Showdown Yahtzee's long-term impact was limited, it demonstrated the ongoing efforts to keep the franchise innovative and engaging.
Licensing deals became a significant driver of Yahtzee's expansion during this period. The introduction of Yahtzee Jr. exemplified this strategy, leveraging popular fictional characters to attract younger players and expand the game's demographic reach. By associating Yahtzee with beloved characters from children's entertainment, the brand sought to cultivate a new generation of players and ensure its relevance in an increasingly competitive market.
However, the most profound shift for Yahtzee in the 1990s was its gradual transition into digital formats. This evolution was driven by the rapid expansion of personal computing and the declining cost of consumer electronics. As more households gained access to computers and handheld electronic devices, Yahtzee adapted to meet changing consumer preferences and technological capabilities.
The appearance of the first handheld electronic Yahtzee games represented a significant milestone. These portable devices offered the classic Yahtzee experience in a compact, digital format, allowing players to enjoy the game on the go without the need for physical dice or scoresheets. This innovation addressed the growing demand for portable entertainment and introduced Yahtzee to a new market of tech-savvy consumers.
Desktop computer editions of Yahtzee further expanded the game's digital presence. These versions brought the familiar gameplay to personal computers, offering enhanced graphics, automated scoring, and the ability to play against computer opponents. The digital format also allowed for new features such as statistical tracking and varying difficulty levels, adding depth to the classic game.

Pokemon Edition
1998
The rise of the internet in the latter half of the decade paved the way for online Yahtzee games. These web-based versions enabled players to compete against opponents from around the world, fostering a global community of Yahtzee enthusiasts. Online play introduced new dynamics to the game, such as real-time multiplayer matches and global leaderboards, enhancing its competitive aspect.
Despite this digital shift, traditional Yahtzee sets remained popular, with many players appreciating the tactile experience of rolling physical dice and marking paper scoresheets. The coexistence of physical and digital versions allowed Yahtzee to cater to a wide range of preferences, bridging generational gaps and technological divides.
The 1990s thus represented a pivotal decade for Yahtzee, as it successfully straddled the line between tradition and innovation. By embracing digital formats while maintaining its classic appeal, Yahtzee positioned itself for continued relevance in the rapidly evolving landscape of gaming and entertainment. This adaptability ensured that as the new millennium approached, Yahtzee remained a beloved game, ready to face the challenges and opportunities of the digital age.
 in the 21st Century
in the 21st Century

2008
As the world nervously awaited Y2K and computer systems worldwide prepared for potential digital chaos, one analog entertainment proved utterly immune to millennium bugs: Yahtzee. While fears of technological collapse dominated headlines at the turn of the century, families gathering around kitchen tables found comfort in the familiar rattle of five dice and the satisfying scratch of pencil on scorecard.
The early 2000s marked a pivotal moment for Yahtzee's cultural expansion. Hasbro's strategy proved prescient: rather than abandoning the tactile pleasure of rolling real dice, they enhanced the core experience while simultaneously exploring new frontiers. The rise of branded editions became a cultural phenomenon unto itself - Spider-Man Yahtzee capitalized on the superhero movie boom that defined much of the decade, while themed versions like NASCAR Yahtzee tapped into America's growing motorsports obsession. These weren't mere cosmetic changes; many incorporated unique scoring systems or special rules that reflected their source material, creating hybrid experiences that honored both the original game's mechanics and the beloved franchises they celebrated.
Meanwhile, the digital revolution that had initially seemed threatening to traditional board games became Yahtzee's greatest ally in reaching new audiences. Online versions flourished on early gaming websites, introducing the game to players who might never have encountered it otherwise. The transition from dial-up to broadband internet made multiplayer Yahtzee sessions possible across continents, transforming what had always been a living room activity into a global pastime.
The game's endurance through the tumultuous early 2000s - surviving not just Y2K fears but also the dot-com crash, 9/11, and massive shifts in how people consumed entertainment - demonstrated something profound about its design. In an era increasingly dominated by complex video games and digital distractions, Yahtzee's elegant simplicity became its greatest strength. Perhaps most remarkably, Yahtzee's success in the 2000s came not from chasing technological trends but from doubling down on what made it special in the first place: the universal human love of games that balance skill with chance, the satisfaction of a perfect roll, and the social connection forged through shared competition.
 in the 2010s
in the 2010s

2012
In the 2010s, Yahtzee underwent a quiet revolution that didn’t involve the familiar clatter of dice on a tabletop. As technology reshaped how people played and connected, Yahtzee found a second life on screens of all sizes. The game’s transition into the digital age preserved its core mechanic - rolling five dice for combinations - but layered in new modes of play, competition, and customization. These innovations helped Yahtzee remain culturally relevant in an era dominated by mobile entertainment.
The most successful of these adaptations has been Yahtzee With Buddies, a mobile app developed by Scopely and launched in 2015. The app introduced asynchronous multiplayer gameplay, daily challenges, collectible dice, and global leaderboards - features designed to appeal to both casual players and dedicated fans. It experienced a massive boom during the COVID-19 pandemic, when homebound users sought accessible, social games. By 2020, the game had surpassed $500 million in lifetime revenue, securing its place as one of the most successful mobile board game adaptations of all time.
Yahtzee's evolution during the 2010s wasn’t limited to mobile screens. The decade also saw a wave of experimental versions that embraced technology and alternative formats. Yahtzee Flash (also known as Yahtzee Turbo) reimagined the game using motion-sensitive electronic dice that lit up and shuffled wirelessly, introducing elements of speed and dexterity. Card-based variations like Yahtzee Hands Down reinterpreted the core mechanics for faster, more portable play. These spin-offs pushed the boundaries of what Yahtzee could be while remaining rooted in its signature five-dice format.
At the same time, Hasbro capitalized on fandom culture by releasing a series of branded, collectible editions. From Star Wars and The Walking Dead to Disney Princesses and Marvel superheroes, these themed sets featured custom dice, scorecards, and packaging tailored to pop culture franchises. While often marketed as novelty items or gifts, they also served to introduce the game to younger players and collectors alike. Whether in digital form, electronic gadgetry, or licensed collectibles, Yahtzee’s enduring appeal in the 2010s came from its remarkable ability to adapt while staying true to its original spirit.
 in the 2020s
in the 2020s

2023
In an era marked by rapid technological change and global economic uncertainty, Yahtzee has remained a reliable bright spot in Hasbro’s portfolio. While many traditional toy and game categories faced headwinds, Yahtzee continued to post strong performance, particularly in the digital and licensing sectors. The brand’s ability to straddle both the physical and virtual worlds has made it unusually resilient, delivering steady returns in an otherwise volatile market.
The momentum of Yahtzee With Buddies carried into the new decade, with ongoing content updates, seasonal tournaments, and community-driven events keeping players engaged across mobile platforms. Its success reflects a broader shift in gaming, where nostalgia, accessibility, and casual competition converge. Meanwhile, Hasbro continued to explore new partnerships and themed editions, bringing Yahtzee into fresh context - from branded party games to streaming-friendly formats that appeal to social media-savvy audiences.
From Roman dice rituals to 20th-century yacht parties to global mobile leaderboards, Yahtzee’s story is one of continual reinvention grounded in timeless simplicity. As long as people are drawn to the suspense of a final roll and the joy of shouting “Yahtzee!” with friends or strangers, the game will continue to endure - not just as a pastime, but as a cultural throughline that connects generations through play.
Learn More about Yahtzee History
If you want to dive even deeper into the fascinating history of Yahtzee, then look no further than The Yahtzee Blog. This comprehensive blog is dedicated to exploring the story of Yahtzee from ancient times to the present day, with in-depth articles, interactive timelines, and expert insights. Enhance your Yahtzee knowledge and learn about the evolution of this classic game by subscribing now!
Whether you're a longtime fan of the game or just getting started, The Yahtzee Blog has something for everyone. The blog is filled with fascinating information about the game, including detailed histories of the equipment used to play, the various scoring strategies that players have developed over the years, and the many different versions of the game that have been released.










