The History of Dice
When were dice invented? A seemingly simple object, yet one imbued with a rich history that stretches back millennia. For Yahtzee enthusiasts like ourselves, understanding the origin story of these little cubes of fate adds a delightful layer of appreciation to every roll. So, put down that scorecard for a moment, fellow Yahtzeeists, and delve into the captivating chronicle of cast bones!
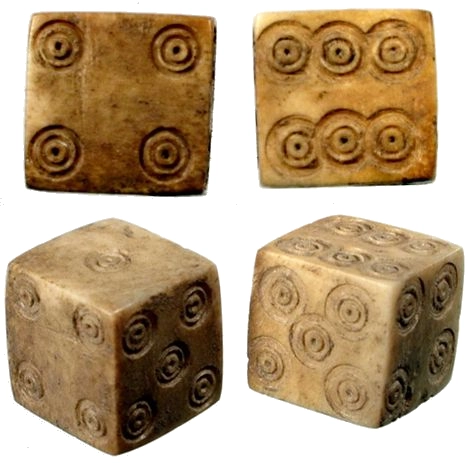

c. 100 CE
In our digital age, random number generation (RNG) is the hidden engine behind countless experiences. From the thrilling chaos of online games to the unblinking impartiality of encryption algorithms, RNG weaves its magic in the background. But the quest for randomness extends far beyond the realm of computers. For millennia, humanity has craved methods to introduce a delightful element of chance into our lives, and dice – those seemingly simple cubes – stand as a testament to this enduring desire. The history of dice is a fascinating journey that transcends entertainment, delving into the realms of divination, mathematics, and even the very fabric of human decision-making. So, before we delve into the clatter and excitement of rolling dice, let's embark on this exploration of their rich and surprising past.
Dice History Highlights
- 3000 BCE (Mesopotamia) - The earliest known six-sided dice are discovered in Sumerian excavations. These dice were often made of clay and were used in both games and rituals.
- 2000 BCE (Egypt) - Dice appear in Egyptian tombs and are depicted in hieroglyphics. The Egyptians primarily used dice for games, although they might have had ceremonial or divinatory purposes as well.
- 1400 BCE (India) - Evidence of early dice games like "Pachisi" (a precursor to Ludo) emerges. Cubical dice become common, and their use spreads through trade routes to Persia and China.
- 600 BCE (Greece) - Dice games become common, often attributed to the legend of Palamedes, who is said to have invented dice during the Trojan War. However, historical records discredit this claim.
- 500 BCE (Rome) - Dice games like "Hazard," a predecessor to modern-day craps, gain popularity among Roman soldiers and civilians. Dice made of ivory, bone, and other materials are commonly found in Roman households.
- 1st Century CE (Roman Empire) - Dice are used extensively for gambling across the Roman Empire. Dice with irregular shapes and "loaded" dice (manipulated to land on certain numbers) also emerge during this period.
- 600 CE (Middle Ages) - Dice continue to be popular in medieval Europe, often used in games like backgammon and hazard. They are also incorporated into divination practices, where rolling dice would help predict the future.
- 17th Century (Renaissance) - The development of mathematical probability theory by figures like Blaise Pascal leads to a better understanding of dice outcomes and randomness, transforming dice gaming into a subject of scientific inquiry.
- 19th Century - With the industrial revolution, dice manufacturing becomes more standardized, leading to fairer dice. This period also sees an increase in the popularity of dice-based games in casinos and parlors.
- 20th Century - Dice become central to tabletop gaming, especially with the rise of games like Monopoly (1930s) and Dungeons & Dragons (1970s), where a variety of polyhedral dice are introduced.
- 21st Century - Dice are widely used in both physical board games and digital formats. Online casinos offer virtual dice-based games, and polyhedral dice have become iconic in the role-playing community.


Dice and Chance
Ah, the allure of randomness! Dice history begins not with the polished plastic cubes we cherish today, but in a time far more primal. Our ancestors, ever the playful bunch, craved a way to inject a dose of delightful uncertainty into their lives. Games became the perfect arena for this, and resourceful as ever, they turned to readily available materials: animal bones.
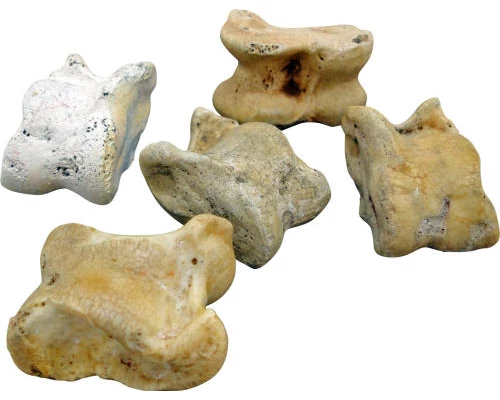

c. 5000 BCE
Enter the knucklebones, most notably the sheep astragalus (ankle bone). These weren't your average playthings. With their naturally uneven surfaces, only a few flat sides could land face-up when tossed. This inherent limitation wasn't a buzzkill, mind you. It introduced a delightful element of controlled chaos. Players, ever the strategists, could begin to predict the most likely landing positions based on the bone's shape and their throwing technique. This delightful blend of chance and cunning added a layer of depth to these early games.
But knucklebone dice weren't the only option in this pre-cubical paradise. Simple sticks, perhaps with one end marked or carved, or even stones with distinct markings, also served as tools of playful randomness. Imagine tossing a marked stick and interpreting the result based on which end landed face-up. Simple, yet undeniably effective in adding a dash of unpredictable fun to their games.
The Rise of the Cube
Fast forward a few millennia, and around 3100-2500 BCE, the world of games takes a fascinating turn. The iconic six-sided cube bursts onto the scene, not just an evolution from knucklebones, but a game-changer offering a more standardized and versatile tool for chance.

c. 2500 BCE
Archaeological digs have unearthed some of the earliest evidence for these cubical dice in two intriguing locations: the Indus Valley Civilization (present-day Pakistan and India) and the Burnt City in Iran. The Indus Valley Civilization, known for its well-planned cities and advanced drainage systems, flourished around 3300-1300 BCE. The Burnt City, located in southeastern Iran, dates back to a similar period and is believed to have been a major trading center.
This geographically diverse spread suggests the innovation wasn't confined to a single area. Perhaps vibrant trade routes or cultural exchange facilitated the dissemination of these exciting new tools for random number generation. Imagine merchants traveling vast distances, bringing not only goods but also the thrill of games played with these little cubes.
Crafted for Play
Unlike readily available knucklebones, these early dice required a bit more effort in their creation. Terracotta, a type of fired clay, emerged as a popular material choice. It was plentiful, durable, and could be easily molded into the desired cube shape. We can only speculate about the artisans who crafted these early dice. Perhaps they chanted or inscribed symbols for good luck on the clay before baking them into instruments of playful fate.
One intriguing feature of these ancient dice is the presence of the "opposing sevens" configuration – the same layout we see on modern dice with the sum of opposite sides always adding up to seven (1 and 6, 2 and 5, etc.). This consistency across such a vast timeframe is truly fascinating.
There are two possible explanations for this design choice:
- Practicality for Balanced Gameplay: Perhaps the opposing sides adding up to seven ensured a fair distribution of possible outcomes, making the games more engaging.
- Symbolism Lost to Time: There's also the possibility that the "opposing sevens" held a deeper symbolic meaning lost to the sands of time. Did the number seven hold some special significance in these ancient cultures? In many cultures around the world, the number seven is associated with completeness, good luck, or even mystical properties. Perhaps the same was true for the civilizations that created these early dice.
Egyptians Join the Crapshoot

c. 600-800 BCE
Evidence from Egyptian tombs dating back to 2000 BCE reveals the presence of cubical and even more complex dice. This suggests the widespread popularity of these tools for chance across geographically diverse regions. Imagine a Pharaoh, adorned with elaborate jewelry and draped in fine linens, locked in a tense dispute with a court official. The weighty decision – land or resources, perhaps even a matter of justice – could hinge on a single, capricious roll of the dice. This adds an element of unpredictable drama to the scene, highlighting the potential seriousness with which games involving dice were taken.
The widespread presence of dice across such geographically diverse cultures underscores their universality as a tool. But were they just for entertainment? There are hints that dice may have served purposes beyond games. Perhaps they were used in divination rituals, where people sought to interpret the will of the gods or predict the future. This possibility adds another layer of intrigue to the story of the cube's rise in ancient times.
The Written Word and the Global Spread of Dice

c. 300 BCE
The first documented reference to dice comes from the epic Indian poem, the Mahabharata, composed around 400 BCE. This suggests that dice were already a well-established part of Indian games by this time. Moving westward, ancient Greece and Rome embraced dice with fervor. Crafted from bone or ivory, they were used in popular games like tali and tesserae. Romans even incorporated dice into their religious practices, seeking divine guidance through the roll. Just imagine, a Roman legionary tossing the dice to determine the outcome of a battle – a practice that undoubtedly added an extra layer of nervous anticipation to the eve of war!
China wasn't immune to the allure of dice either. Polyhedral dice, including the cube, were used in games like liubo, a pastime enjoyed during the Zhou Dynasty era. Even medieval Europe, despite occasional disapproval from religious authorities, saw dice flourish as a popular form of entertainment and even gambling.

Beyond Games: Faith & Science of Dice
Dice weren't always content to decide winners and losers. In many cultures, they transcended entertainment, becoming a conduit to the divine. This practice, divination, used seemingly random events to glean whispers from the cosmos. Dice, with their capricious rolls, became a bridge between humanity and the unseen forces that governed their world.
Imagine a Roman soldier, on the eve of battle, consulting a priest who throws the dice. The resulting numbers weren't just pips on a cube; they were omens, messages from the gods themselves. A favorable roll signified Jupiter's blessing, while an unlucky throw might hint at Mars' disapproval. The outcome of the dice roll could have a profound impact, influencing morale, strategy, and even the decision to go to war.
Across Africa, dice played a similar role in rituals and ceremonies. The specific practices varied, but the core concept remained the same: using the randomness of the dice to connect with the spirit world and determine the course of events. A single roll could diagnose illness, identify misfortune's source, or even choose a leader. The dice, imbued with a near-sacred quality, held the potential to shape a community's destiny.
This use of dice speaks to humanity's enduring fascination with the unknown. We crave control over our destinies, and in the absence of answers, we turn to rituals and tools like dice to bridge the gap. The exact methods used in dice divination remain shrouded in mystery, but the historical evidence leaves little doubt about their significance. Those seemingly simple cubes hold a legacy of seeking answers in the face of the unknown, a testament to our enduring desire to understand the world around us.
Mathematical Analysis of Dice
The 17th century witnessed a fascinating evolution for the humble die. No longer just a tool for games and divination, it became a subject of fascination for brilliant minds like Galileo Galilei and Girolamo Cardano. These mathematicians delved into the complexities of chance, meticulously analyzing the probabilities associated with dice rolls. Their groundbreaking work laid the foundation for probability theory, a field that would come to revolutionize many areas of study.
Fast forward a few centuries, and we encounter Yatzie, the game's fascinating forerunner, emerging in the early 20th century. Yatzie, believed to be a descendant of earlier dice games like Yacht and Generala, established many of the core elements that Yahtzee players know and love today. The familiar scoring system, with its emphasis on rolling specific combinations, found its roots in Yatzie. The iconic dice cup, used to ensure fair and random rolls, also became a staple element during this era.
It's a testament to the enduring appeal of this core mechanic – the thrill of rolling dice and strategically creating specific combinations – that Yatzie would evolve into the modern Yahtzee we cherish today. The game's journey, from its ancient origins to its mathematical analysis and eventual commercialization, highlights the enduring human desire for both entertainment and a deeper understanding of the world around us.

Dice in the Industrial Age and Beyond

As gambling regulations tightened in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the demand for precision dice grew. Casinos in both Europe and the United States required perfectly balanced dice to ensure fair play and minimize cheating. This era saw significant advancements in manufacturing, with materials like celluloid, Bakelite, and early plastics replacing traditional bone and wood. These innovations paved the way for more durable and uniform dice, setting new standards in gaming.
The early 20th century saw the rise of the American dice industry, with companies like H.C. Evans & Co. and Midwest Game Supply specializing in casino-grade dice. However, dice were not limited to the gaming floors of legal establishments. During Prohibition (1920–1933), underground gambling dens thrived, creating a black-market demand for dice suppliers. By World War II, dice had found yet another role—mass-produced for soldiers' gambling kits and board games, offering troops a form of entertainment amid the hardships of war.
The late 20th century ushered in a new chapter in dice history, particularly for role-playing games (RPGs). One of the most influential figures of this era was Lou Zocchi, a pioneer in polyhedral dice production. In the 1970s, Zocchi founded Gamescience, producing sharp-edged, high-precision dice designed to roll more fairly than traditional rounded-edge counterparts. His innovations helped fuel the growth of Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) and other tabletop RPGs, cementing dice as essential tools for storytelling and strategy.
As RPGs surged in popularity during the 1980s, Chessex Manufacturing emerged as one of the leading dice companies. Known for their vibrant colors, unique designs, and mass-produced polyhedral sets, Chessex became a staple in gaming communities worldwide. Meanwhile, advancements in technology transformed the dice industry once again. 3D printing and CNC machining now allow for highly customized, one-of-a-kind dice, catering to collectors and enthusiasts looking for more than just standard plastic.
Today, dice continue to evolve, with luxury materials, digital dice apps, and innovative designs reshaping the gaming landscape. From the precision dice of early casinos to the handcrafted RPG dice of modern artisans, the journey of dice reflects both the evolution of gaming and the endless pursuit of fair, functional, and beautifully crafted randomness.

Random Number Generation

The continual spread of electronic Yahtzee online to all corners of the globe brings joy to billions. But the rise of digital dice rolling comes with risks. Imperfections aside, dice are the original random number generators. How do you program randomness into a computer program? While the clatter of physical dice across a tabletop has long been the gold standard for unpredictability, replicating this level of chance in the digital realm proves to be a formidable task.
The Quest for Digital Randomness
At its core, a true random number generator (TRNG) should produce numbers that are entirely unpredictable and uninfluenced by external factors. However, the very nature of electronic devices, with their deterministic processes and algorithmic foundations, creates a paradox in the pursuit of genuine randomness.
The challenge extends beyond mere number generation. Factors such as temperature fluctuations within the hardware, electromagnetic interference from nearby devices, and even minute manufacturing flaws can introduce subtle biases into the system. These biases, while often imperceptible to the casual user, can potentially be exploited by those with malicious intent or a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms.
The Dice Advantage
Traditional dice, particularly in generating numbers from one to six, offer a mechanical means of achieving randomness that has stood the test of time. The complex interplay of physical forces – gravity, air resistance, the initial force of the throw, and the subtle imperfections of the dice themselves – creates a system that is remarkably difficult to predict or replicate consistently.
This level of unpredictability has made dice the cornerstone of games like Yahtzee for generations. The tactile experience of rolling dice, coupled with the inherent trust in their randomness, adds a layer of excitement and fairness that digital alternatives struggle to match.

Digital Alternatives and Their Limitations
In the digital realm, developers have devised various methods to generate numbers that are "random enough" for most applications. These approaches range from deterministic algorithms that use seed values to create seemingly random sequences, to more sophisticated systems that tap into physical sources of randomness such as thermal noise or atmospheric disturbances.
Computational random number generators, while capable of producing vast sequences of pseudo-random numbers, ultimately face limitations. Even the most powerful machines eventually encounter storage constraints, leading to inevitable repetitions in their number sequences. While these high-quality pseudo-random systems are sufficient for many games and everyday tasks, they fall short of the true randomness required for unbreakable cryptographic systems.
Pushing the Boundaries of Randomness
The quest for true random number generation has led researchers to explore cutting-edge technologies. Some of the most advanced systems, such as those utilizing quantum phenomena or tiny lasers, can produce staggering amounts of random data – up to 250 terabytes of random bits per second. These breakthroughs offer tantalizing glimpses into a future where digital randomness might finally approach the unpredictability of physical dice.
Hardware-based TRNGs represent another avenue of exploration. These systems leverage physical phenomena as sources of randomness, such as measuring the time intervals between radioactive decay events or the voltage fluctuations in diodes affected by thermal noise. While these sources aren't entirely predictable or repeatable, they present significant challenges for any potential attackers attempting to guess or manipulate the generated numbers.
The State of Online Gaming
Many computer games, including online versions of Yahtzee, rely on algorithmic random number generators. While these systems create a convincing illusion of randomness for most players, they ultimately fall short of true unpredictability. The sophistication of these RNG systems can vary widely between different electronic Yahtzee games. Basic models might simply shuffle through a limited set of number combinations, while more advanced versions employ complex computational techniques to simulate randomness.
This variance in RNG quality raises questions about the validity of high scores and exceptional plays in electronic Yahtzee games. The reliability of these achievements is intrinsically tied to the quality of the underlying random number generation system.
Despite the rapid advancements in digital technology, the evidence from dice history remains compelling. The world's original random number generators – physical dice – continue to outperform modern computers in terms of true unpredictability. For purists seeking the most authentic Yahtzee experience, disconnecting from the digital world and returning to physical dice remains the gold standard.
The Future of Yahtzee and Random Number Generation
As Yahtzee continues to evolve beyond its tabletop origins, adapting to new technologies and platforms, the question of randomness remains at the forefront. Game publishers strive to meet the growing demand for online Yahtzee experiences, potentially exploring cutting-edge technologies like virtual reality to bridge the gap between digital convenience and physical authenticity.
The future of random number generation in gaming holds exciting possibilities. As quantum computing becomes more accessible, we may see quantum random number generators incorporated into online games, offering a level of unpredictability that rivals physical dice. AI-enhanced systems might be developed to detect and correct subtle biases in RNG outputs, ensuring fairness across millions of digital dice rolls.
Balancing Tradition and Innovation
While the World Yahtzee Institute emphasizes the unique benefits of physical dice and face-to-face social interaction, the advantages of online play cannot be ignored. The convenience of instant access, the diversity of game variations and opponents, and the global social connections facilitated by online platforms offer compelling reasons to embrace digital Yahtzee.
For those seeking to refine their skills, experiment with strategies, or simply enjoy a quick game without the need for physical dice, online versions provide an invaluable resource. As technology continues to advance, we may see new hybrid systems that combine the tactile satisfaction of physical dice with the convenience and advanced randomness of digital systems, offering players the best of both worlds.
In the end, whether rolling physical dice across a kitchen table or generating random numbers through sophisticated algorithms, the spirit of Yahtzee endures. The game continues to captivate players with its perfect blend of chance and strategy, proving that sometimes, the simplest concepts can lead to the most enduring forms of entertainment.

A Legacy Set in Stone: Dice Continue to Roll On
The history of dice is a captivating tapestry woven with threads of entertainment, divination, and even mathematical exploration. From their humble beginnings as animal bones to their sophisticated role in probability theory, dice continue to be a source of enjoyment, suspense, and friendly competition.
So, the next time you gather around the table with your Yahtzee crew, take a moment to appreciate the rich heritage embedded within those seemingly simple cubes. After all, every roll is not just a test of luck, but a connection to a millennia-old tradition. It's a testament to our enduring fascination with chance, a desire to inject a delightful element of randomness into our lives.
And while the materials and methods have evolved – from terracotta cubes to plastic injected with tiny air pockets to influence fairness – the core principle remains the same. Each toss, each click of the dice cup, is a nod to our ancestors who first embraced the thrill of randomness. In that unpredictable moment, we connect not only with our fellow players, but also with the long line of history stretching back millennia, all united by the captivating roll of the dice.